[TOC]
Overview
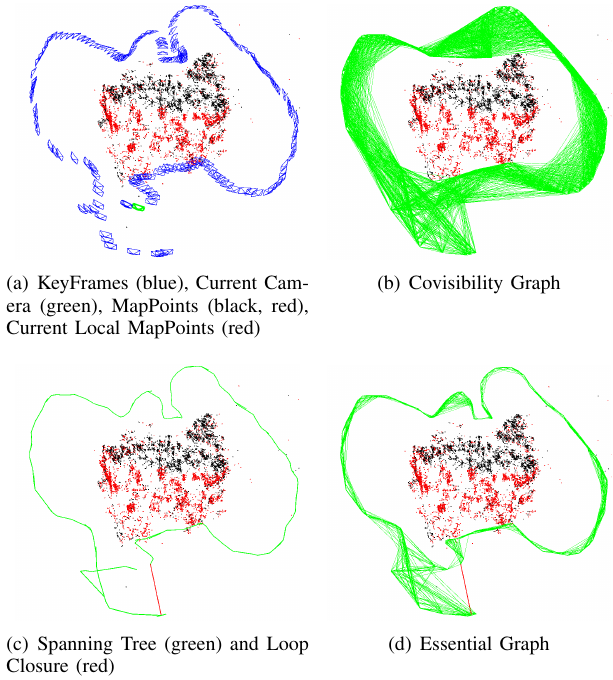
Map Points & KeyFrames
- Each keyframe $K_i$ stores
-
ID
static long unsigned int nNextId; long unsigned int mnId; const long unsigned int mnFrameId; - camera pose
- camera intrinsics
-
KeyPoints related
// Number of KeyPoints const int N; // KeyPoints, stereo coordinate and descriptors (all associated by an index) const std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> mvKeys; const std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> mvKeysUn; const std::vector<float> mvuRight; // negative value for monocular points const std::vector<float> mvDepth; // negative value for monocular points const cv::Mat mDescriptors; // BoW DBoW2::BowVector mBowVec; DBoW2::FeatureVector mFeatVec; -
MapPoints associated to keypoints
std::vector<MapPoint*> mvpMapPoints; void KeyFrame::AddMapPoint(MapPoint *pMP, const size_t &idx) { unique_lock<mutex> lock(mMutexFeatures); mvpMapPoints[idx] = pMP; }
-
- Each map point $P_i$ stores
-
ID
long unsigned int mnId; static long unsigned int nNextId; long int mnFirstKFid; long int mnFirstFrame; -
Reference KeyFrame (TODO: Anchor Frame?)
KeyFrame* mpRefKF; - 3D position
cv::Mat mWorldPos; - Mean viewing direction
cv::Mat mNormalVector; - Best descriptor to fast matching
cv::Mat mDescriptor; -
The maximum and minimum distances
// Scale invariance distances float mfMinDistance; float mfMaxDistance; -
Keyframes observing the point and associated index in keyframe
std::map<KeyFrame*,size_t> mObservations; int nObs; void MapPoint::AddObservation(KeyFrame* pKF, size_t idx) { unique_lock<mutex> lock(mMutexFeatures); if(mObservations.count(pKF)) return; mObservations[pKF]=idx; if(pKF->mvuRight[idx]>=0) nObs+=2; else nObs++; } -
Tracking counters
int mnVisible; int mnFound;
-
exigent culling mechanism
-
MapPoints
void LocalMapping::MapPointCulling(); -
KeyFrame
void LocalMapping::KeyFrameCulling();
Covisible Graph (KeyFrame Connections)
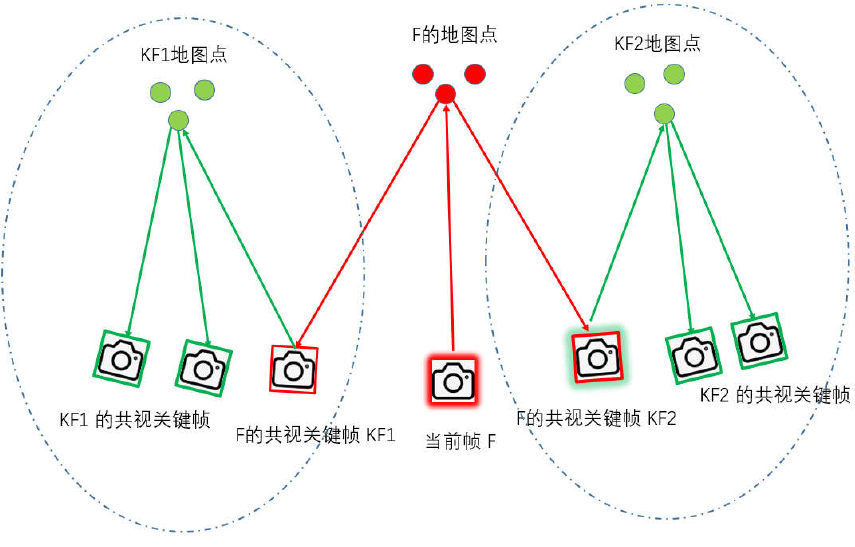
Covisibility information between keyframes is very useful in several tasks of our system, and is represented as an undirected weighted graph.
- Node (KeyFrame)
- Edge (Weight): 关键帧之间共视的 路标点数,至少15
std::map<KeyFrame*,int> mConnectedKeyFrameWeights;
// Covisibility graph functions
void AddConnection(KeyFrame* pKF, const int &weight);
void EraseConnection(KeyFrame* pKF);
void UpdateConnections();
void UpdateBestCovisibles();
std::set<KeyFrame *> GetConnectedKeyFrames();
std::vector<KeyFrame*> GetVectorCovisibleKeyFrames();
std::vector<KeyFrame*> GetBestCovisibilityKeyFrames(const int &N);
std::vector<KeyFrame*> GetCovisiblesByWeight(const int &w);
int GetWeight(KeyFrame* pKF);
Spanning Tree
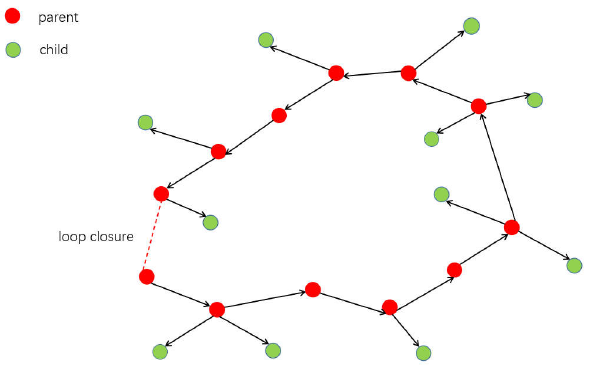
The system builds incrementally a spanning tree from the initial keyframe, which provides a connected subgraph of the covisibility graph with minimal number of edges. When a new keyframe is inserted, it is included in the tree linked to the keyframe which shares most point observations, and when a keyframe is erased by the culling policy, the system updates the links affected by that keyframe.
- Parent Node:
KeyFrame* mpParent;, the pair with highest covisibility weight - Child Nodes:
std::set<KeyFrame*> mspChildrens;
// Spanning tree functions
void AddChild(KeyFrame* pKF);
void EraseChild(KeyFrame* pKF);
void ChangeParent(KeyFrame* pKF);
std::set<KeyFrame*> GetChilds();
KeyFrame* GetParent();
bool hasChild(KeyFrame* pKF);
- TrackLocalMap 里 UpdateLocalKeyFrames更新局部地图中的关键帧
- 闭环矫正时 优化 Essential Graph
Loop Edges
std::set<KeyFrame*> mspLoopEdges;
// Loop Edges
void AddLoopEdge(KeyFrame* pKF);
std::set<KeyFrame*> GetLoopEdges();
Essential Graph
The Essential Graph contains the spanning tree, the subset of edges from the covisibility graph with high covisibility ($\theta_{min} = 100$), and the loop closure edges, resulting in a strong network of cameras.
- Node (KeyFrame)
- Edge
- Spanning tree edges
- Covisibility graph edges (weight > 100):
pKF->GetCovisiblesByWeight(100) - Loop edges