Overview
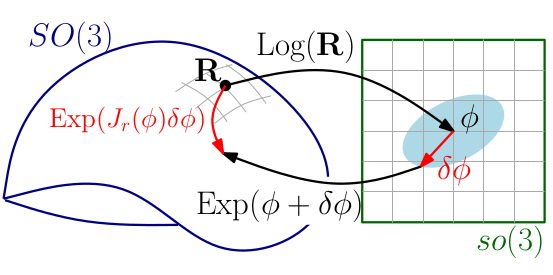
Manifold Space vs Tangent Space
Jacobian w.r.t Error State
Jacobian w.r.t Error State vs True State
According 1 2.4,
\[f(x \boxplus \delta)=f(x)+J_x \delta+\mathcal{O}\left(\|\delta\|^2\right)\]The idea is that for a $x \in N$ the function $g(\delta) := f (x \boxplus \delta)$ behaves locally in $0$ like $f$ does in $x$. In particular $|f(x)|^2$ has a minimum in $x$ if and only if $|g(\delta)|^2$ has a minimum in $0$. Therefore finding a local optimum of $g$, $\delta = \arg \min_{\delta} |g(\delta)|^2$ implies $x \boxplus \delta = \arg \min_{\xi} |f(\xi)|^2$.
where
\[J = \left. \frac{\partial f(x \boxplus \delta)}{\partial \delta} \right|_{\delta=0} \quad \longleftrightarrow \quad J = \left. \frac{\partial f(x)}{\partial x} \right|_{x}\]
ESKF 2 6.1.1: Jacobian computation
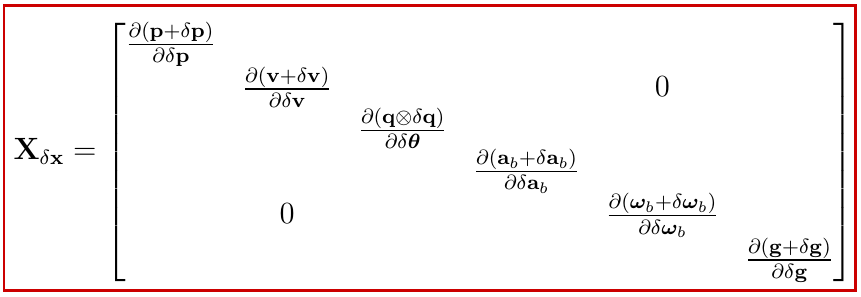
\[\left.\mathbf{H} \triangleq \frac{\partial h}{\partial \delta \mathbf{x}}\right|_{\mathbf{x}}=\left.\left.\frac{\partial h}{\partial \mathbf{x}_t}\right|_{\mathbf{x}} \frac{\partial \mathbf{x}_t}{\partial \delta \mathbf{x}}\right|_{\mathbf{x}}=\mathbf{H}_{\mathbf{x}} \mathbf{X}_{\delta \mathbf{x}}\]- $x_t$: true state
- $x$: normal state
- $\delta x$: error state
lifting and retraction:
the quaternion term
\[\begin{aligned} \left.\mathbf{Q}_{\delta \boldsymbol{\theta}} \triangleq \frac{\partial(\mathbf{q} \otimes \delta \mathbf{q})}{\partial \delta \boldsymbol{\theta}}\right|_{\mathbf{q}} &=\left.\left.\frac{\partial(\mathbf{q} \otimes \delta \mathbf{q})}{\partial \delta \mathbf{q}}\right|_{\mathbf{q}} \frac{\partial \delta \mathbf{q}}{\partial \delta \boldsymbol{\theta}}\right|_{\delta \hat{\boldsymbol{\theta}}=0} \\ &=\left.\left.\frac{\partial\left([\mathbf{q}]_L \delta \mathbf{q}\right)}{\partial \delta \mathbf{q}}\right|_{\mathbf{q}} \frac{\partial\left[\begin{array}{c} 1 \\ \frac{1}{2} \delta \boldsymbol{\theta} \end{array}\right]}{\partial \delta \boldsymbol{\theta}}\right|_{\hat{\delta}=0} \\ &=[\mathbf{q}]_L \frac{1}{2}\left[\begin{array}{lll} 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right] \end{aligned}\]Least Squares on a Manifold 3
Local Parameterization in Ceres Solver 4 5 6 7 8
class LocalParameterization {
public:
virtual ~LocalParameterization() = default;
virtual bool Plus(const double* x,
const double* delta,
double* x_plus_delta) const = 0;
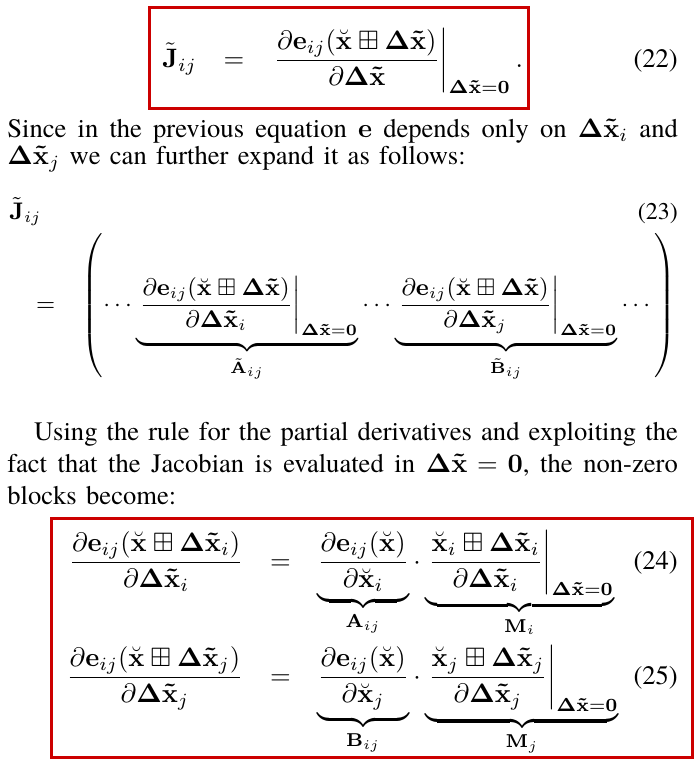
virtual bool ComputeJacobian(const double* x, double* jacobian) const = 0;
virtual bool MultiplyByJacobian(const double* x,
const int num_rows,
const double* global_matrix,
double* local_matrix) const;
virtual int GlobalSize() const = 0;
virtual int LocalSize() const = 0;
};
Plus
Retraction
\[\boxplus(x, \Delta)=x \operatorname{Exp}(\Delta)\]ComputeJacobian
global w.r.t local
\[J_{GL} = \frac{\partial x_G}{\partial x_L} = D_2 \boxplus(x, 0) = \left. \frac{\partial \boxplus(x, \Delta)}{\partial \Delta} \right|_{\Delta = 0}\]参考 9
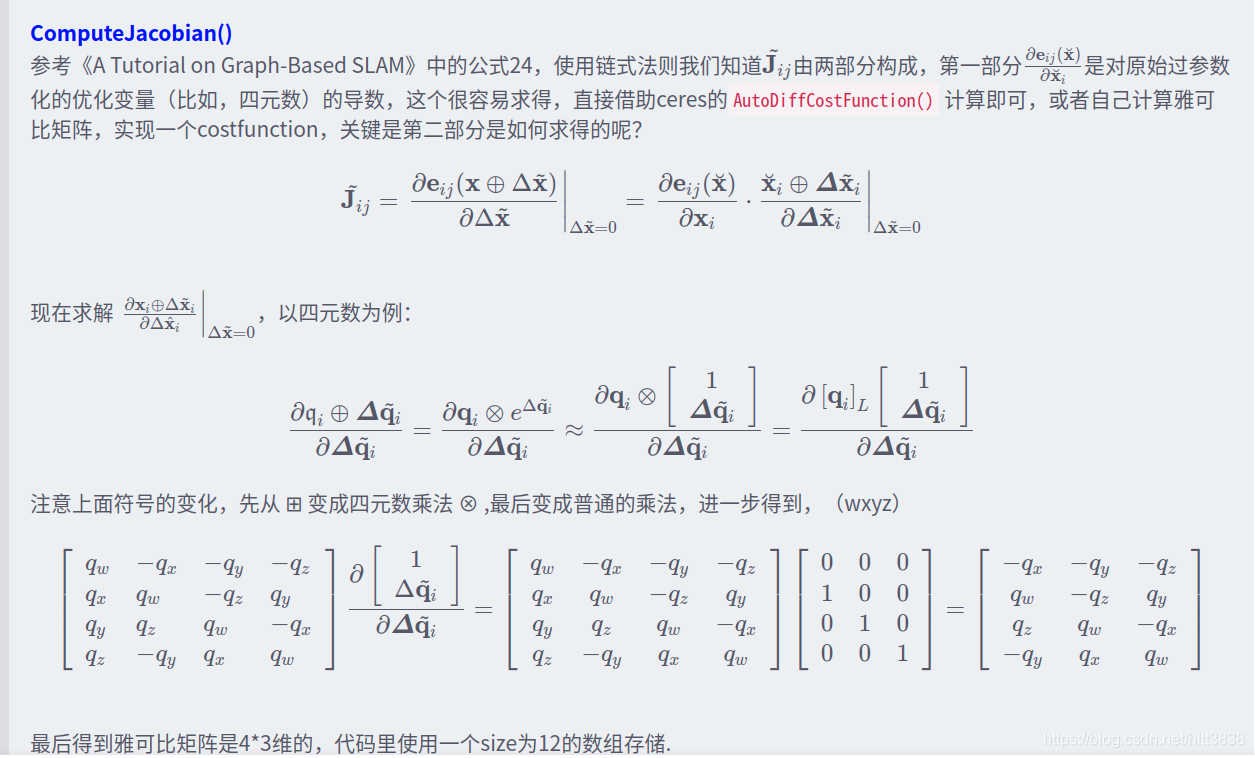
$r$ w.r.t $x_{L}$
在 ceres::CostFunction 处提供 residuals 对 Manifold 上变量的导数
则 对 Tangent Space 上变量的导数
\[J_{rL} = \frac{\partial r}{\partial x_L} = \frac{\partial r}{\partial x_G} \cdot J_{GL}\]Sub Class
- QuaternionParameterization
- EigenQuaternionParameterization
自定义 QuaternionParameterization
参考 7

Summary
- QuaternionParameterization 的 Plus 与 ComputeJacobian 共同决定使用左扰动或使用右扰动形式
Quaternion in Eigen
Quaterniond q1(1, 2, 3, 4); // wxyz
Quaterniond q2(Vector4d(1, 2, 3, 4)); // xyzw
Quaterniond q3(tmp_q); // xyzw, double tmp_q[4];
q.coeffs(); // xyzw
Quaternion in Ceres Solver
- order:
wxyz - Ceres Solver 中 Quaternion 是 Hamilton Quaternion,遵循 Hamilton 乘法法则
- 矩阵 raw memory 存储方式是 Row Major
-
A Framework for Sparse, Non-Linear Least Squares Problems on Manifolds ↩
-
Quaternion kinematics for the error-state Kalman filter, Joan Solà ↩
-
A Tutorial on Graph-Based SLAM ↩
-
http://ceres-solver.org/nnls_modeling.html#localparameterization ↩
-
[ceres-solver] From QuaternionParameterization to LocalParameterization
 ↩ ↩2
↩ ↩2 -
LocalParameterization子类说明:QuaternionParameterization类和EigenQuaternionParameterization类 ↩