[TOC]
Overview
digraph {
TV [label="TextureView"];
TVs [label="N TextureViews"];
Texturing [style=filled, shape=box];
ColorImg->TV;
CamK->TV;
CamTF->TV;
TV->TVs;
TVs->Input;
TriangleMesh->Input;
Input->Texturing->Output->TexturedMesh;
}
- code (forked): https://github.com/cggos/mvs-texturing
- paper: Let There Be Color! Large-Scale Texturing of 3D Reconstructions
- video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ie-qLJdmlLI
1. Texture Views
tex::generate_texture_views()
digraph {
TV [label="TextureView"];
TV->ColorImg;
TV->CamK;
TV->CamTF;
}
2. Mesh –> MeshInfo
tex::prepare_mesh()
Check Mesh
TriangleMesh::ensure_normals()
- Ensure face and vertex normals
Init MeshInfo
MeshInfo::initialize()
Create VertexInfo
Add faces to their three vertices
digraph {
vertex -> face1
vertex -> face2
vertex -> face3
}
Update VertexInfo
Classify each vertex and compute adjacenty info
- Build new, temporary adjacent faces representation
AdjacentFaceList adj_tempfor ordering
digraph {
face_id [color=green];
front_vid [color=blue];
back_vid [color=blue];
AdjFaceTmp->face_id
AdjFaceTmp->front_vid
AdjFaceTmp->back_vid
}
graph {
layout=twopi;
node [shape=circle];
v0 [color="red"];
v1 [color="blue"];
v2 [color="blue"];
v0--v1 [color=green];
v0--v2 [color=green];
v0--v3;
v0--v4;
v1--v2 [color=green];
v3--v2;
v3--v4;
v1--v4;
overlap=false;
}
-
Sort adjacent faces by chaining them
AdjacentFaceList adj_sorted; -
update
VertexInfo
digraph {
vclass;
verts [color=blue];
faces [color=green];
vinfo->vclass;
vinfo->verts;
vinfo->faces;
}
3. Mesh + MeshInfo –> Adjacency Graph (UniGraph)
tex::build_adjacency_graph()
对于每个 face,将mesh中与其每条 edge 邻接的 face 存入 adj_faces;将当前 face 与 adj_faces 中每个 face 建立 edge,构建 UniGraph 。
graph {
node [shape=circle];
f0--f1; f1--f2;
f0--f3; f3--f4;
f1--f4;
overlap=false;
}
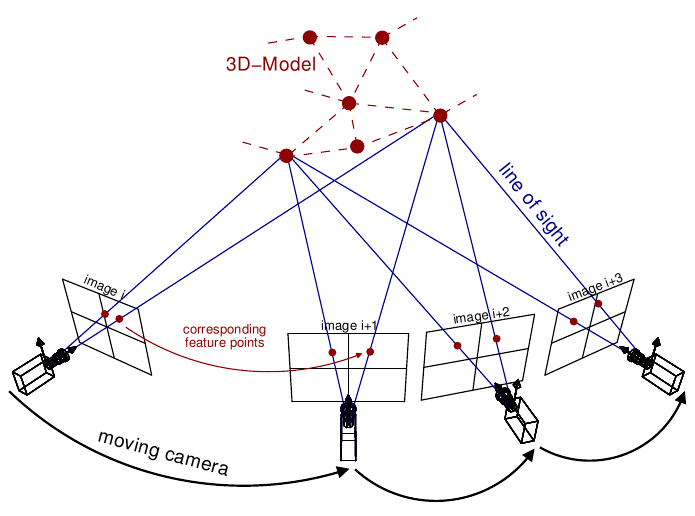
4. View Selection –> Best View Label 
tex::calculate_data_costs()
tex::view_selection()
Calculate DataCosts
Calculates the data costs for each face and texture view combination, if the face is visible within the texture view.
FaceProjectionInfos face_projection_infos(num_faces);
calculate_face_projection_infos(mesh, texture_views, settings, &face_projection_infos);
postprocess_face_infos(settings, &face_projection_infos, data_costs);
Calculate FaceProjectionInfo
for (std::uint16_t j = 0; j < static_cast<std::uint16_t>(num_views); ++j) {
TextureView * texture_view = &texture_views->at(j);
// get view_pos and view_dir
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < faces.size(); i += 3) {
// get face_normal and face_center
// compute and check viewing_angle
// get face info
}
}
digraph {
face_info [style=filled];
nnn [label="..."];
face_info_n [style=filled];
rankdir=LR;
face_id->face_info;
face_info->view_id;
face_info->mean_color;
face_info->quality;
face_id->nnn;
face_id->face_info_n;
}
PostProcess Face Infos
create hist_qualities::Histogram using info.quality, and get the upper_bound when percentile=0.995
compute data cost
- gmi
- area
float normalized_quality = std::min(1.0f, info.quality / percentile);
float data_cost = (1.0f - normalized_quality);
data_costs->set_value(i, info.view_id, data_cost);
| DataCost | face0 | face1 | … | faceN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| view0 | ||||
| view1 | ||||
| … | ||||
| viewN |
View Selection
Data Association
Graph mapmap::Graph<cost_t>
graph {
rankdir = LR;
face_id--adj_face_id [label="weight"];
}
LabelSet mapmap::LabelSet<cost_t, simd_w>
| view id | face0 | face1 | … | faceN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| view0 | ||||
| view1 | ||||
| … | ||||
| viewN |
Unaries
using unary_t = mapmap::UnaryTable<cost_t, simd_w>;
std::vector<unary_t> unaries;
| face_id | label_set | costs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| unary0 | |||
| unary1 | |||
| … | |||
| unaryN |
Pairwise
using pairwise_t = mapmap::PairwisePotts<cost_t, simd_w>;
pairwise_t pairwise(1.0f);
MAP-MRF 
mapmap::mapMAP<cost_t, simd_w> solver;
solver.set_graph(&mgraph);
solver.set_label_set(&label_set);
for(std::size_t i = 0; i < graph->num_nodes(); ++i)
solver.set_unary(i, &unaries[i]);
solver.set_pairwise(&pairwise);
solver.set_logging_callback(display);
solver.set_termination_criterion(&terminate);
solver.optimize(solution, ctr);
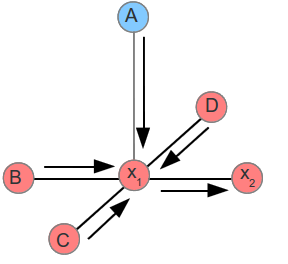
The aim is to find a labeling for X that produces the lowest energy.
pairwise MRFs
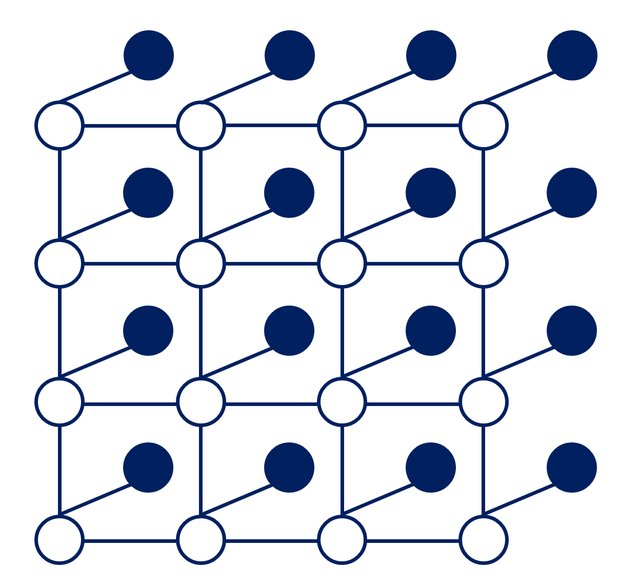
- the filled-in circles: the observed nodes $Y_i$ (face)
- the empty circles: the “hidden” nodes $X_i$ (view label)
MAP –> Minimum Energy
energy/cost function:
\[\text{energy} (Y, X) = \sum_{i} \text{DataCost} (y_i, x_i) + \sum_{j = \text{neighbours of i}} \text{SmoothnessCost} (x_i, x_j)\]Tree MRFs via DP
LBP
by OpenMVS
5. Create Texture Atlases 
tex::generate_texture_patches()
tex::global_seam_leveling()
tex::local_seam_leveling()
tex::generate_texture_atlases()
Generate Texture Patches
Generates texture patches using the graph to determine adjacent faces with the same label.
Global / Local Seam Levelling 
- paper: Seamless Mosaicing of Image-Based Texture Maps
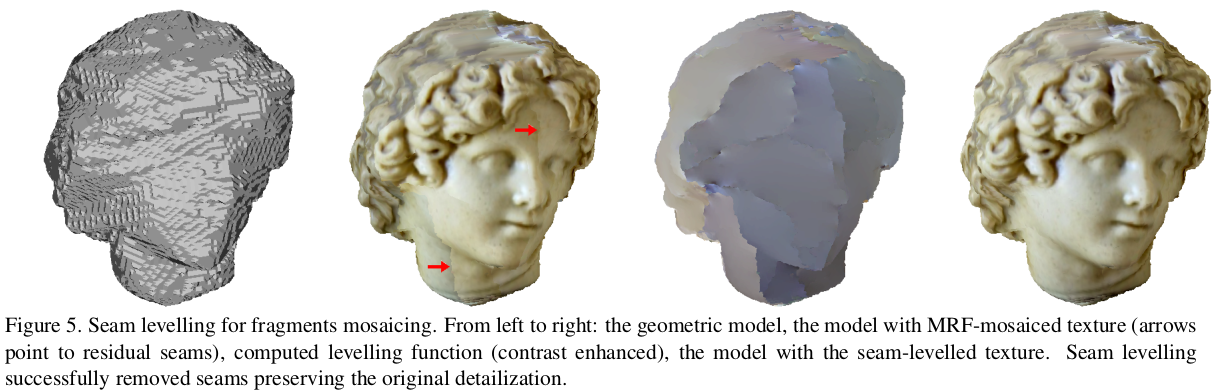
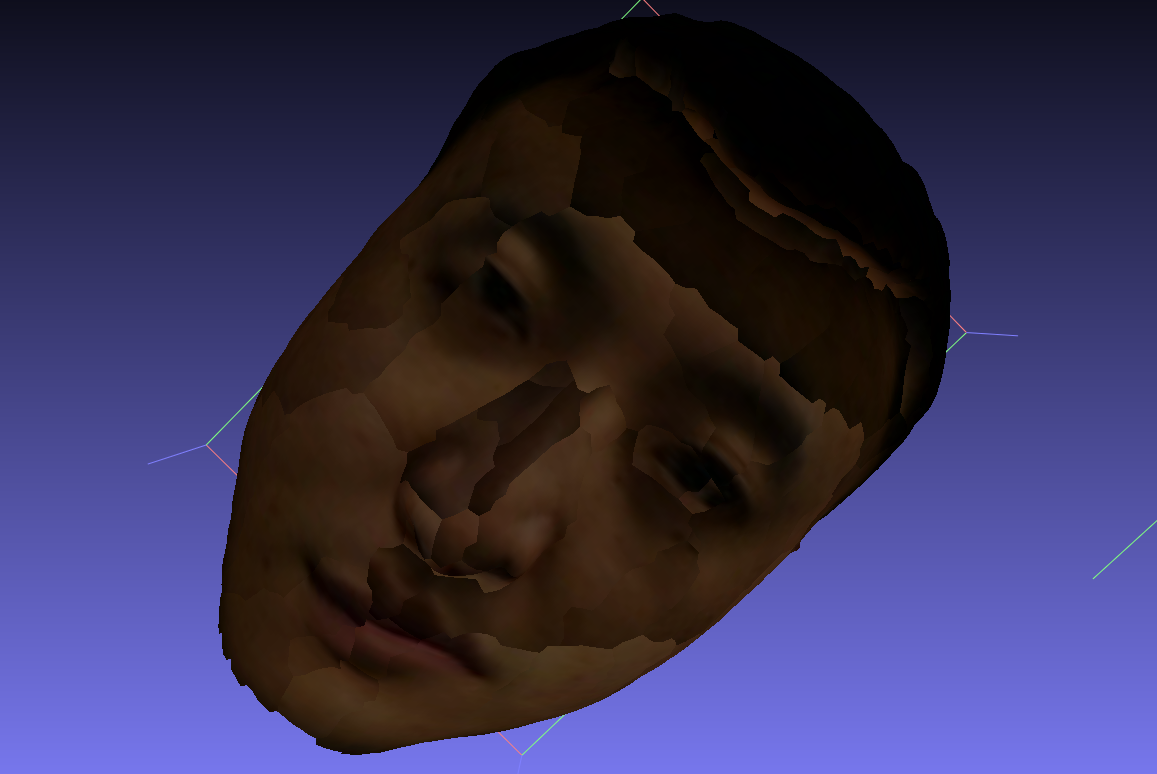
without seam levelling

Texture Atlases
generate TextureAtlas from all of TexturePatch

6. Mesh + Texture –> Obj Model
tex::build_model()
tex::Model::save()
- .obj
- .mtl
- .png
网格UV展开
上述纹理重建属于 计算机视觉 的内容,本节是其逆过程,属于 计算机图形学 的内容。
- http://geometryhub.net/notes/uvunfold
Reference
- UV的概念及作用
- 【Let It Be Color!——3D重建之纹理重建】02-基于映射的纹理重建算法(上)
- https://github.com/tyluann/3DTexture
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44424934